Key Takeaways:
The Google Home 4.8 update marks a meaningful shift in how smart homes operate in 2026, moving beyond simple voice commands toward more adaptive, context-aware automation. Instead of requiring constant manual setup, the platform now emphasizes learning patterns, reducing friction, and coordinating devices more intelligently across the home. For users already invested in connected devices, this update is less about flashy additions and more about making everyday automation finally feel reliable and intuitive.
Introduction: Why This Update Matters More Than It Looks
Smart home platforms often promise intelligence but deliver complexity. Over the past few years, many households accumulated connected lights, thermostats, cameras, and speakers, only to discover that managing them required ongoing attention. Automations broke, routines conflicted, and minor changes in daily habits caused systems to fail silently.
What makes the Google Home 4.8 release relevant is not a single headline feature, but a structural rethink of how automation should adapt to people rather than the other way around. Most coverage focuses on surface-level additions, yet misses the deeper implication: Google is recalibrating its approach to smart homes around behavioral signals, cross-device awareness, and reduced setup overhead. For tech-savvy homeowners in 2026, this update signals a transition from “programmable homes” to “responsive environments.”
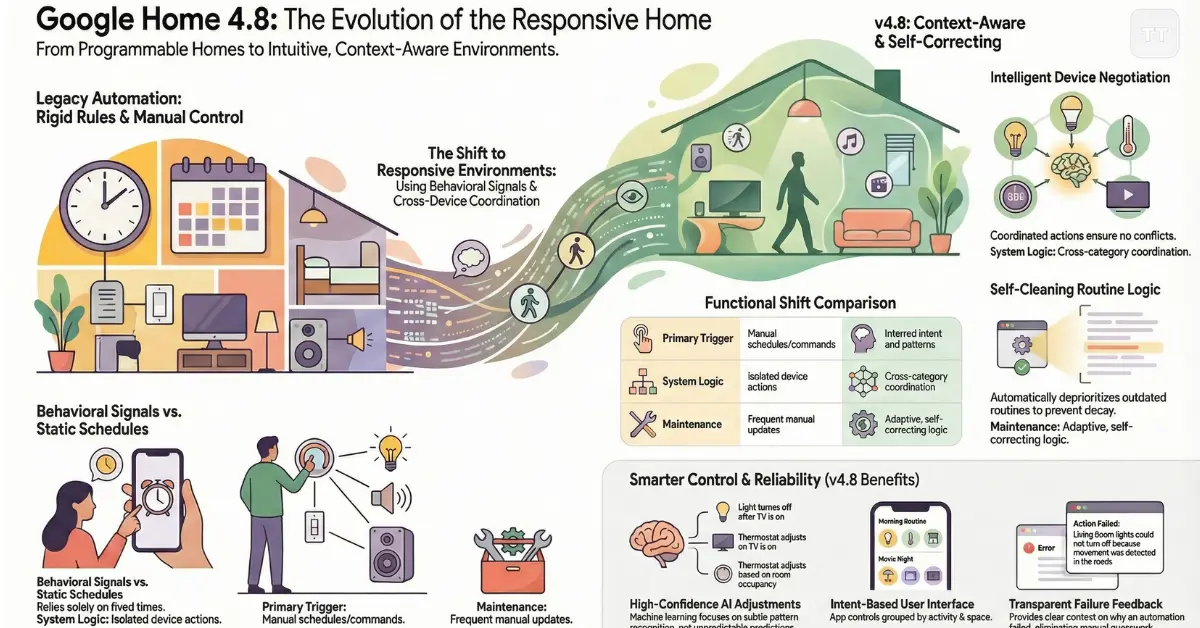
From Rule-Based Routines to Context-Aware Behavior
Earlier versions of Google Home relied heavily on explicit triggers. Users defined conditions, set schedules, and hoped nothing changed. In practice, this rigidity limited adoption beyond enthusiasts willing to troubleshoot.
The current iteration leans into contextual interpretation. Instead of asking whether a routine should run at exactly 7:00 a.m., the system increasingly evaluates signals such as device usage patterns, presence detection, and environmental changes. Lights, climate control, and media playback now coordinate more fluidly, particularly in multi-user households where schedules rarely align.
This evolution does not eliminate manual routines, but it changes their role. Custom setups now act as guardrails rather than scripts, allowing the system to adapt within defined boundaries instead of failing outright when conditions shift.
What Has Actually Changed Inside Home Automation
Smarter Coordination Between Devices
One of the less visible but most impactful improvements is how devices negotiate actions with one another. Previously, a command affecting one category—lighting, for example—often ignored the state of other systems. The updated platform places more emphasis on coordination, ensuring that changes in one area do not unintentionally disrupt another.
For example, adjusting lighting scenes now considers active media playback and room occupancy more consistently. This reduces the common frustration of automations triggering at the wrong time or clashing with ongoing activities.
Reduced Dependency on Manual Triggers
Manual triggers remain available, but the system increasingly favors inferred intent. This is particularly noticeable in recurring daily scenarios such as mornings, evenings, and transitions between home and away states. The result is fewer duplicated routines and less maintenance over time.
However, this shift introduces a tradeoff. Users accustomed to absolute predictability may notice slight variations in behavior as the system adapts. The update favors relevance over rigidity, which aligns better with real households but may feel unfamiliar at first.
Routines That Learn, Not Just Run
The Google Home routines upgrade in this version reflects a broader industry trend toward adaptive automation. Instead of treating routines as static sequences, the platform now adjusts execution based on recent patterns and device feedback.
This is most apparent in homes with diverse device ecosystems. Heating, lighting, and security routines now respond to seasonal changes and usage history with fewer manual adjustments. Over time, the system prioritizes routines that consistently deliver value while deprioritizing those that are frequently overridden.
An overlooked detail is how this affects long-term usability. Many smart homes degrade over time as outdated routines accumulate. By gradually reshaping which automations take precedence, the platform reduces this decay, making mature setups more stable rather than more fragile
AI-Driven Automation Without the Gimmicks
Smart home AI automation has often been marketed aggressively, yet delivered inconsistently. The 4.8 update takes a quieter approach, focusing on incremental intelligence rather than overt “AI modes.”
Machine learning is applied primarily to pattern recognition and anomaly detection. Instead of attempting to predict everything, the system concentrates on high-confidence adjustments—such as recognizing habitual device usage or detecting when automations repeatedly fail to execute as intended.
This conservative deployment matters. Overly aggressive automation can erode trust quickly. By limiting AI-driven changes to areas where confidence is high, the platform avoids the uncanny behavior that previously turned users back to manual controls.
The Google Home App Experience in 2026
Subtle Interface Changes With Practical Impact
The Google Home app new features are less about visual redesign and more about functional clarity. Device states are easier to interpret at a glance, and automation controls are grouped more logically around intent rather than device type.
This reduces cognitive load, particularly for users managing larger homes or mixed-brand ecosystems. The app now better reflects how people think about spaces and activities rather than individual gadgets.
Faster Troubleshooting and Feedback Loops
One improvement that receives little attention is how the app communicates failures. When automations do not run as expected, the system provides clearer context about why. This transparency helps users refine setups without resorting to trial-and-error.
For advanced users, this creates a more collaborative relationship with the platform. Instead of guessing what went wrong, adjustments become data-informed decisions.
Smart Home Automation in 2026: Broader Implications
The smart home automation update 2026 reflects a maturation phase for the category. Growth is no longer driven by adding more devices, but by making existing ecosystems less demanding to maintain.
This has implications beyond convenience. Energy efficiency, accessibility, and household coordination all benefit when automation becomes adaptive rather than prescriptive. Homes respond more naturally to irregular schedules, guests, and lifestyle changes without constant reconfiguration.
At the same time, increased automation intelligence raises questions about transparency and control. The platform attempts to balance autonomy with oversight, but users should remain aware of how much decision-making they delegate.
Common Misconceptions Around the Update
A frequent assumption is that more intelligence automatically means less control. In practice, the update preserves manual overrides and customization, while shifting the default experience toward adaptability.
Another misconception is that benefits only apply to new hardware. While certain capabilities improve with newer devices, many changes are software-driven and extend to existing setups. This makes the update more inclusive than typical platform refreshes.
Finally, some expect dramatic visual changes. The reality is more understated, prioritizing stability and coherence over novelty. This may feel anticlimactic at first, but tends to age better over time.
Who Benefits Most—and Who Might Not
This update is particularly valuable for households with multiple users, varied schedules, and diverse device categories. The more dynamic the environment, the more noticeable the improvements become.
Conversely, minimal setups with a few devices and simple routines may see limited immediate impact. In such cases, the value emerges gradually as habits shift or device counts increase.
Understanding this distinction helps set realistic expectations. The update is designed to scale with complexity rather than transform simple setups overnight.
Upgrade your home audio & smart assistant setup today with Google Home: Buy Now
Frequently Asked Questions
Does the update change how voice commands work?
Voice control remains familiar, but responses are more context-aware. Commands are interpreted with greater sensitivity to current activities and device states.
Is additional hardware required to access new automation capabilities?
Most features are software-based and work with existing compatible devices, though newer hardware may unlock more precise sensing.
Can users disable adaptive automation if preferred?
Adaptive behaviors can be limited or overridden through routine settings, preserving manual control where desired.
Does this affect privacy or data usage?
Automation improvements rely on on-device and account-level signals, with controls available to manage data sharing preferences.
Is setup more complex than before?
Initial setup remains straightforward, with complexity shifting away from configuration and toward ongoing adaptation.
Conclusion: A Quieter but More Meaningful Evolution
The Google Home 4.8 update does not attempt to redefine smart homes overnight. Instead, it addresses long-standing friction points that prevented automation from feeling genuinely helpful. By emphasizing adaptability, coordination, and restraint, the platform moves closer to fulfilling its original promise.
For users willing to let their systems evolve gradually, this update offers a more resilient and less demanding smart home experience. As connected environments become more integrated into daily life, this kind of understated progress may prove more valuable than any single breakthrough feature.


