Summary:
In 2026, AI chatbots have evolved into operational partners that support decision-making, automate workflows, and coordinate complex systems across organizations. The challenge is no longer identifying whether AI assistants are useful, but determining which platforms deliver reliable intelligence, governance, and long-term value for specific business needs. The best-performing solutions distinguish themselves through integration depth, contextual reasoning, and trustworthiness rather than conversational fluency alone.
Why AI Chatbots Matter More in 2026 Than Ever Before
AI chatbots are no longer evaluated as standalone tools. In modern organizations, they increasingly function as connective tissue between people, data, and software. As work becomes more distributed and software stacks more fragmented, AI assistants reduce friction by translating intent into coordinated action.
What many discussions still overlook is that this shift has changed the risk profile of chatbot adoption. When assistants influence forecasts, customer responses, or operational decisions, errors carry real consequences. As a result, the market has moved away from novelty-driven experimentation toward deliberate, outcome-focused adoption.
This explains why the conversation around intelligent assistants in 2026 centers on reliability, explainability, and alignment with organizational workflows—not just raw model intelligence.
From Conversational Interfaces to Operational Intelligence
The most advanced conversational AI tools now operate less like chat windows and more like orchestration layers. They interpret requests, trigger actions across systems, monitor outcomes, and adapt future responses based on feedback.
For example, a business analyst may ask an assistant to identify revenue anomalies, draft an executive summary, and notify stakeholders—all within a single interaction. The assistant’s value lies not in answering one question, but in coordinating multiple systems without requiring the user to manage complexity.
This capability has become a defining feature of next-generation AI chatbots.
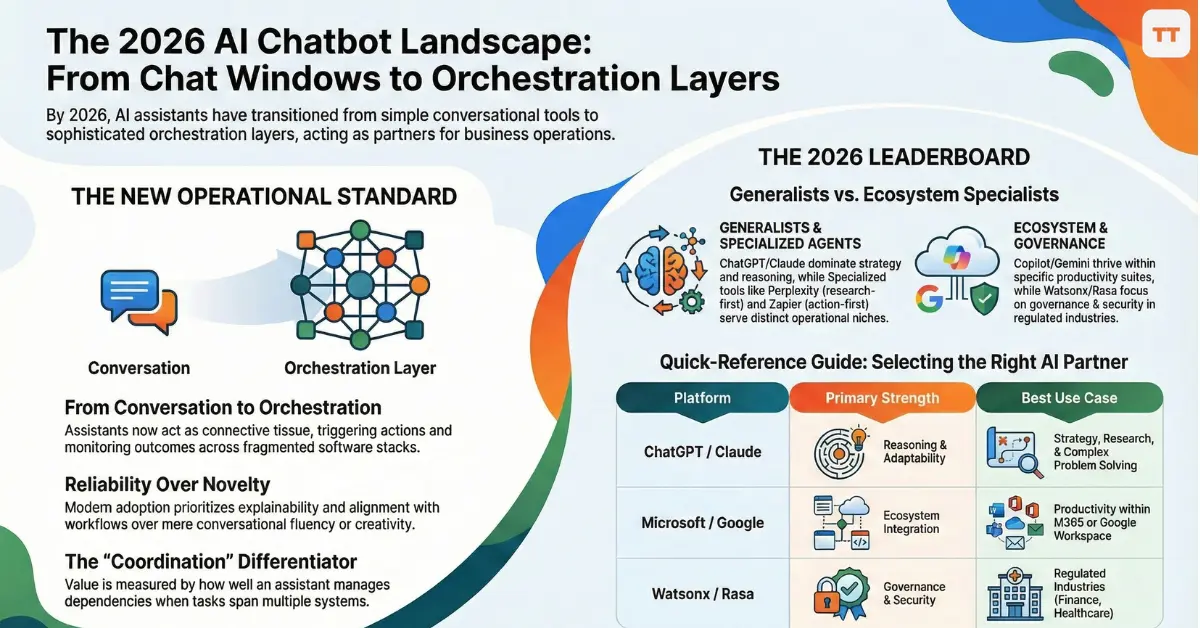
How the Top AI Chatbots in 2026 Compare in Practice
Rather than ranking assistants purely by intelligence, it is more useful to evaluate them by how they are adopted and trusted in real environments. The following platforms consistently emerge as leaders across business productivity, automation, and enterprise deployment in 2026.
Top 10 AI Chatbots in 2026
1. ChatGPT (OpenAI)
ChatGPT remains one of the most widely adopted AI assistants due to its broad reasoning ability, adaptability, and expanding ecosystem. It is commonly used for strategy development, writing, research, coding, and agent-based automation. Its strength lies in versatility, making it suitable for cross-functional teams that need a single assistant capable of handling diverse tasks.
ChatGPT is often chosen by organizations that value flexibility and rapid experimentation, though governance configuration is critical in regulated environments.
2. Claude (Anthropic)
Claude is recognized for structured reasoning, long-context understanding, and careful language generation. It is frequently used for policy analysis, technical documentation, and complex problem-solving where clarity and constraint matter.
Businesses that prioritize precision over breadth often gravitate toward Claude, particularly for internal knowledge work and analytical tasks where misinterpretation carries downstream risk.
3. Google Gemini
Gemini’s primary advantage lies in its deep integration with Google’s productivity and data ecosystem. It excels in collaborative environments where real-time documents, search, and multimodal inputs intersect.
Organizations already embedded in Google Workspace often find Gemini a natural extension of existing workflows, particularly for research-heavy or collaborative use cases.
4. Microsoft Copilot
Microsoft Copilot has become a central productivity layer for enterprises using Microsoft 365. By operating directly within tools like Word, Excel, Outlook, and Teams, it reduces context switching and accelerates everyday work.
Copilot’s strength is not creative range, but embedded utility. It is frequently adopted by large organizations seeking incremental productivity gains without altering existing software habits.
5. Perplexity AI
Perplexity AI positions itself as a research-first assistant, emphasizing source-aware responses and real-time information synthesis. It is commonly used for competitive analysis, market research, and evidence-based decision support.
This assistant appeals to professionals who value transparency in how conclusions are formed and who need to trace insights back to underlying sources.
6. DeepSeek Chat
DeepSeek has gained attention for its open and developer-friendly approach, offering strong reasoning capabilities with a focus on customization and data control. It is particularly attractive to teams that want flexibility without relying entirely on closed ecosystems.
Its growing adoption reflects a broader trend toward configurable assistants that can be tailored to specific operational needs.
7. Zapier AI Agents
Zapier’s AI agents blur the line between chatbots and automation engines. Rather than serving primarily as conversational tools, they coordinate actions across thousands of applications using natural language triggers.
These agents are especially valuable for operations teams and small businesses that want to automate workflows without heavy engineering investment.
8. Meta AI
Meta AI is increasingly embedded across messaging and social platforms, supporting conversational commerce, customer engagement, and content interaction. Its strength lies in scale and accessibility rather than enterprise-grade governance.
It is most commonly used in marketing, community management, and consumer-facing interactions where reach and immediacy matter.
9. Rasa (Enterprise Custom Deployments)
Rasa remains a leading choice for organizations that require full control over conversational logic, data handling, and deployment environments. Rather than offering a fixed assistant, Rasa enables teams to build bespoke solutions aligned with internal policies.
This approach is often favored in industries where compliance, customization, and transparency outweigh convenience.
10. IBM Watsonx Assistant
Watsonx Assistant continues to serve organizations in regulated sectors such as finance, healthcare, and government. Its emphasis on security, auditability, and enterprise governance makes it a dependable choice for mission-critical deployments.
While it may lack the flexibility of general-purpose assistants, its reliability and compliance posture remain key differentiators.
What These Leaders Reveal About the Market
The diversity of this list highlights an important reality: there is no universal “best” AI assistant. Instead, leaders emerge within distinct adoption patterns.
General-purpose assistants dominate strategy and creative work. Embedded assistants thrive in productivity environments. Custom platforms succeed where governance and control are paramount. Understanding these distinctions prevents costly mismatches between tools and expectations.
Automation Is No Longer the Differentiator
In 2026, automation is assumed. The real differentiator is coordination—how well an assistant manages dependencies, context, and escalation when tasks span systems or teams.
Assistants that merely automate steps save time. Those that coordinate intent reduce cognitive load. Over time, the latter produce far greater organizational leverage.
A Commonly Overlooked Limitation: Context Drift
Even the most advanced AI assistants can suffer from context drift during long-running projects. Assumptions made early may persist silently, influencing outputs in subtle ways.
Teams that periodically reset goals and constraints tend to maintain better alignment. This reframes assistants not as self-correcting entities, but as collaborators that benefit from intentional recalibration.
Trust, Transparency, and Long-Term Adoption
Trust has become a defining competitive advantage among enterprise AI chatbot platforms. Organizations increasingly favor assistants that can signal uncertainty, explain reasoning boundaries, and respect permission scopes.
These qualities rarely dominate marketing materials, yet they strongly influence whether an assistant becomes deeply embedded or quietly sidelined after initial rollout.
How AI Chatbots Fit Into Broader Business Strategy
AI assistants increasingly act as primary interfaces to complex systems. This raises a strategic question: should they remain tools, or become foundational infrastructure?
Organizations that treat assistants as infrastructure—designing workflows around them rather than bolting them on—tend to extract compounding value over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes one AI chatbot better than another in 2026?
The most effective assistants combine reasoning quality, integration depth, and trust controls rather than excelling in conversation alone.
Are AI chatbots suitable for enterprise-wide deployment?
Yes, provided governance, permissions, and data boundaries are clearly defined and enforced.
Can a single AI assistant serve all business needs?
In practice, many organizations use multiple assistants tailored to different functions rather than relying on one universal solution.
How long does it take to see value from AI chatbots?
Initial productivity gains often appear quickly, but the most significant benefits emerge once workflows are redesigned around the assistant.
Do AI chatbots replace traditional software?
They rarely replace software outright. Instead, they reduce friction by acting as an intelligent interface across existing tools.
Conclusion: Redefining “Best” in the Age of Intelligent Assistants
The idea of the best AI chatbot in 2026 cannot be reduced to rankings or feature lists. Value emerges from alignment—between assistant capabilities, organizational culture, and real-world constraints.
Teams that approach AI assistants as strategic partners rather than novelty tools tend to make better decisions and achieve more durable outcomes. The true advantage lies not in choosing the most powerful model, but in selecting the assistant that fits how work actually happens.
As AI continues to evolve, the organizations that thrive will be those that design for collaboration between humans and systems, rather than expecting intelligence alone to solve complexity.