Summary
Google Android 17 Beta 1 introduces early platform refinements, expanded AI integration, and deeper privacy controls aimed at developers preparing for 2026 device cycles. The release focuses less on visual redesign and more on performance consistency, background execution changes, and smarter on-device intelligence. For teams building or maintaining apps, this beta is primarily about compatibility validation and forward-looking feature alignment.
A Release That Signals Direction, Not Just Features
Every major Android beta carries two layers: what users see and what the platform is quietly becoming. Google Android 17 Beta 1 clearly leans toward the second. While incremental UI adjustments exist, the real story lies in system behavior, AI acceleration pathways, and tighter guardrails around background processes.
Most early coverage tends to focus on visible features. What is often missed is how beta cycles subtly redefine app expectations—particularly around energy efficiency, privacy declarations, and AI-assisted workflows. Android 17 appears designed for a future where on-device models are standard, not experimental, and where background resource usage is scrutinized more aggressively than before.
For developers and IT decision-makers, this release is less about novelty and more about risk management and strategic preparation.
What Actually Changes in Android 17 Beta 1
The Android 17 Beta 1 features set reflects refinement rather than disruption. Several enhancements are evolutionary but strategically important.
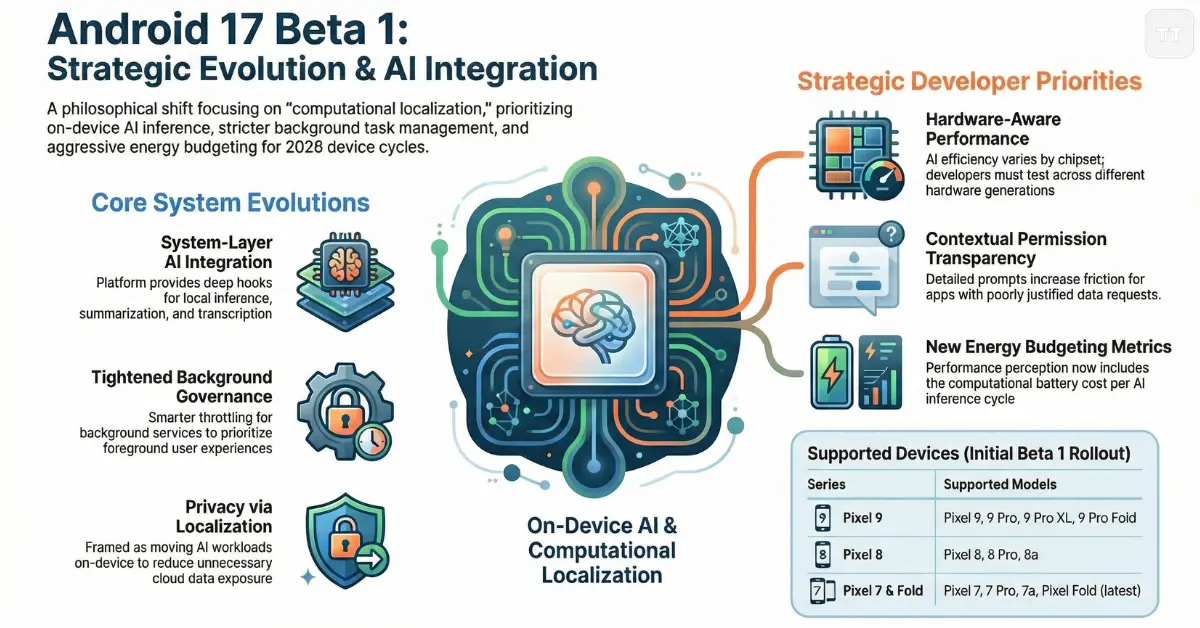
1. Background Task Governance Tightened Further
Android has gradually restricted background execution since Android 8.0. Android 17 continues that trajectory by introducing smarter throttling for background services tied to non-visible activities.
Apps that rely on persistent background polling, especially for location or network updates, may notice stricter scheduling windows. In testing environments, this could surface delayed event triggers or missed sync intervals if not optimized properly.
This signals an ongoing platform philosophy: foreground experience first, silent consumption last.
2. AI Framework Integration at the System Layer
Android 17 privacy and AI updates represent one of the most meaningful changes in this cycle. Rather than treating AI as an optional extension, the platform now provides deeper system-level hooks for on-device inference.
Improvements include:
- More efficient Tensor acceleration pathways on supported hardware
- Expanded APIs for local summarization, transcription, and contextual suggestions
- Standardized fallback logic when on-device inference fails
This shift has two implications:
- Apps that ignore on-device AI capabilities may begin to feel outdated.
- Privacy expectations increase because inference is increasingly local.
Developers should evaluate whether existing AI features rely unnecessarily on cloud calls when equivalent local inference now performs adequately.
3. Subtle UI Behavior Refinements
While not a visual overhaul, Android 17 introduces micro-adjustments to gesture responsiveness, predictive navigation, and adaptive theming stability.
These refinements improve perceived performance more than raw benchmarks do. Beta testers have observed smoother transition interpolation in gesture-based navigation, especially when switching between heavy apps.
The takeaway: perceived fluidity is being optimized as aggressively as measurable speed.
Android 17 Supported Devices List: Who Gets Early Access?
As expected, Pixel devices remain first in line. The Android 17 supported devices list currently includes:
- Pixel 9 Series
- Pixel 8 and Pixel 8 Pro
- Pixel 8a
- Pixel 7 Series
- Pixel Fold (latest generation)
Broader OEM adoption will likely follow in developer preview channels before public beta expansion.
It is worth noting that early beta availability does not guarantee identical AI feature performance across devices. Tensor-powered Pixels may deliver different AI efficiency results compared to older chipsets.
For enterprise IT environments, this matters: compatibility testing should consider hardware generation differences, not just OS version.
Read More: Google Pixel 9a — Product Info & Reviews
How to Install Android 17 Beta (Without Breaking Your Workflow)
For developers and beta testers, how to install Android 17 Beta depends on whether the device is primary or secondary.
The two main paths include:
- Enrolling through the Android Beta Program (OTA updates)
- Flashing factory images manually using Android Flash Tool
OTA enrollment remains the safer path for most testers. However, manual flashing offers cleaner environments for debugging.
A critical decision factor is rollback risk. Beta installations may require full device wipes to revert. Production devices tied to critical authentication systems or enterprise management policies should not be upgraded casually.
The overlooked risk: authentication apps and enterprise device management tools sometimes lag behind OS betas. Teams using mobile device management solutions should validate compatibility before large-scale beta testing.
Android 17 Developer Changes That Demand Attention
Android 17 developer changes primarily affect three areas: background execution, AI APIs, and permission granularity.
Permission Transparency Expands Again
Users now receive more contextual prompts explaining why specific data is accessed. While this improves trust, it increases friction for poorly justified permission requests.
Apps that previously relied on vague permission explanations may see higher denial rates.
This reinforces a broader pattern: permissions must be directly tied to visible functionality.
Stricter Broadcast Receiver Handling
Implicit broadcasts are further limited. Developers using legacy broadcast receivers for system events should verify that listeners remain triggered under new restrictions.
Migration toward more explicit registration patterns is increasingly necessary.
Enhanced Memory Diagnostics
Android 17 introduces improved memory tracking tools within Android Studio integration, offering more granular insight into transient memory spikes.
This is particularly valuable for AI-heavy apps performing local inference, where RAM pressure can silently degrade performance.
Privacy and AI Updates: A Philosophical Shift
Android 17 privacy and AI updates reveal a deeper philosophical evolution.
Rather than treating privacy as restriction, the platform increasingly frames it as computational localization. AI workloads are encouraged to run on-device, reducing cloud exposure.
However, this creates a tradeoff:
- On-device inference improves privacy.
- It increases hardware dependency and may strain lower-end devices.
Developers must decide whether to:
- Offer adaptive AI features based on hardware capability
- Maintain uniform cloud-based AI experiences
- Or combine both approaches with intelligent fallbacks
The strongest long-term strategy appears hybrid: local-first when possible, cloud-enhanced when necessary.
What Most Articles Overlook: Energy Budgeting
A subtle but important shift in Android 17 is energy budgeting. AI acceleration, background restriction, and system smoothing all connect to battery optimization.
Apps that aggressively use AI inference without batching tasks may see unexpected energy penalties.
Energy efficiency is no longer just about network calls. It now includes computational cost per inference cycle.
Developers should test:
- Repeated inference loops
- Idle AI background triggers
- Memory churn under sustained usage
In 2026, performance perception includes battery longevity as much as responsiveness.
Strategic Testing Priorities for Developers
Testing Android 17 Beta 1 should focus on:
- Background task reliability under stricter scheduling
- Permission prompt clarity and denial handling
- AI feature fallback logic
- Memory usage during inference
- Battery impact across long sessions
Rather than testing every feature blindly, developers should simulate real-world scenarios: unstable networks, low battery states, device thermal throttling.
That is where unexpected regressions appear.
Enterprise Considerations: Upgrade Now or Wait?
For IT leaders and enterprise app teams, early adoption depends on business risk tolerance.
Beta adoption is worthwhile when:
- Apps rely heavily on background services
- AI features are core product differentiators
- Compliance requirements depend on privacy enhancements
However, mission-critical production apps should wait for at least Beta 2 or RC stability before recommending broad deployment.
The difference between early curiosity and strategic testing should be clear. Enthusiasts upgrade for exploration. Enterprises upgrade for validation.
A Common Misconception About Beta Releases
Many assume beta releases are mainly about flashy features. In reality, they are about identifying breakpoints.
Android 17 Beta 1 appears stable but still enforces behavior changes that could expose weak architecture patterns—particularly in older apps built before Android’s stricter background policies.
The biggest risk is not crashes. It is silent degradation: delayed notifications, slower sync cycles, or inconsistent AI responses.
These issues rarely show in superficial testing.
Where Android 17 Fits in the Broader Platform Evolution
Looking at the trajectory from Android 13 through Android 16, a pattern emerges:
- Reduced background freedom
- Increased local intelligence
- Higher permission transparency
- Greater battery discipline
Android 17 reinforces that direction rather than diverging from it.Googl
This suggests that future Android versions may further standardize on-device AI toolkits and push developers toward adaptive, context-aware app behavior.
Apps that remain static in design philosophy may struggle in future cycles.
People Also Reader: Is the Google Pixel 10 Pro XL Worth It?
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Google Android 17 Beta 1 stable enough for daily use?
It is relatively stable but not recommended for primary production devices. Minor bugs, performance inconsistencies, and app compatibility issues may still occur.
Which devices are included in the Android 17 supported devices list?
Primarily recent Pixel models, including the Pixel 9, Pixel 8 series, Pixel 8a, Pixel 7 series, and the latest Pixel Fold. Wider OEM support typically follows later beta phases.
How to install Android 17 Beta safely?
Enroll through the Android Beta Program for OTA updates or use the Android Flash Tool for manual installation. Testing should ideally occur on a secondary device to avoid workflow disruption.
What are the most important Android 17 developer changes?
The most impactful changes involve stricter background execution policies, expanded AI system integration, enhanced memory diagnostics, and more transparent permission prompts.
Do Android 17 privacy and AI updates affect app performance?
Yes, especially for apps using local AI inference. On-device processing improves privacy but may increase computational load, requiring optimization and hardware-aware scaling.
The Real Opportunity in Android 17 Beta 1
Google Android 17 Beta 1 is less about transformation and more about alignment. It aligns Android with a future where AI runs locally, permissions are explicit, background activity is constrained, and energy efficiency defines performance.
Developers who treat this beta as a checklist update may miss its larger implications. Those who use it to rethink AI architecture, background strategies, and energy budgeting will likely build apps that feel native to the next generation of Android devices.
The platform is not just adding features. It is narrowing the definition of what a well-behaved app looks like in 2026


